Introduction to Manual Transmission

Source: onallcylinders.com
Understanding manual transmission gear ratios and their effects – A manual transmission, often called a stick shift, is a type of gearbox that allows a driver to directly control the power flow from the engine to the wheels. This is achieved through a series of gears that can be engaged by the driver to adjust the speed and torque output of the vehicle. Understanding the intricacies of manual transmissions is crucial for efficient and controlled driving.The fundamental principle behind a manual transmission is the use of gear ratios.
These ratios determine how much engine speed is translated into wheel speed, and vice versa. By selecting different gear combinations, drivers can optimize performance for various driving conditions, from accelerating on a highway to navigating a steep hill. This control is a significant advantage over automatic transmissions.
Manual Transmission Components
Manual transmissions are comprised of several key components working together to transfer power. Understanding their roles is essential for grasping the overall operation.
- Clutch: This mechanical component disengages the engine from the transmission. It allows for shifting between gears without causing a sudden jolt to the vehicle. A common analogy is that the clutch acts as a break between the engine and transmission, enabling smooth gear changes. Modern clutches are often hydraulically assisted for ease of operation.
- Gears: A set of toothed gears, each with a specific gear ratio, form the core of the transmission. Different gear combinations result in various output speeds and torques. This allows for a broad range of driving conditions.
- Shifting Mechanism: The driver operates a lever or a series of buttons to engage different gear combinations. This is crucial for selecting the appropriate gear for the desired speed and torque.
- Transmission Housing: The housing contains and protects all the internal components. It also provides structural support.
- Input Shaft: The input shaft receives power from the engine’s crankshaft. This power is transferred to the transmission for processing.
- Output Shaft: The output shaft transfers the power to the drive axle, ultimately to the wheels.
Gear Ratios and Their Purpose
Gear ratios are the fundamental mechanism for controlling the power flow. They represent the relationship between the input and output speeds of the gears. A gear ratio of 2:1, for example, means that for every two revolutions of the input shaft, the output shaft rotates once.
Gear Ratio = (Number of teeth on driven gear) / (Number of teeth on driving gear)
The purpose of gear ratios is to adjust the speed and torque output of the transmission to match the driving conditions. Higher gear ratios result in lower speeds but higher torque. Lower gear ratios result in higher speeds but lower torque.
Basic Manual Transmission Diagram
The following diagram illustrates a simplified layout of a manual transmission. Note that this is a simplified representation and actual transmissions may have more complex designs. The components are interconnected to transfer power efficiently.
[Diagram: A simple block diagram showing the input shaft, output shaft, gears, clutch, and shifting mechanism. Clearly label each component. The diagram should visually show how power flows from the input to the output, with the shifting mechanism acting as a selector between the various gear ratios.]
Understanding Gear Ratios

Source: gotodobbs.com
Gear ratios are fundamental to understanding how a manual transmission works. They dictate the relationship between the engine’s output and the wheels’ speed and torque, enabling the driver to select the optimal gear for various driving conditions. Different gear ratios allow for a wide range of speeds and power delivery, making the car suitable for both low-speed maneuvers and high-speed highway driving.Gear ratios essentially act as a multiplier for both the engine’s rotational speed and the torque it delivers to the wheels.
A higher gear ratio translates to a slower speed of the wheels for a given engine speed, but with a higher torque output. Conversely, a lower gear ratio yields a faster wheel speed, but with a lower torque output. This interplay of speed and torque is crucial for optimal vehicle performance in different driving situations.
Relationship Between Gear Ratios and Speed/Torque
Gear ratios directly influence the speed and torque delivered to the drive wheels. A higher gear ratio means a slower wheel speed for a given engine speed, but a greater torque output. This is vital for tasks requiring significant torque, like accelerating from a standstill or climbing steep hills. Conversely, a lower gear ratio yields a faster wheel speed, but a lower torque output.
This is beneficial for high-speed driving, where maintaining a steady speed with less engine strain is crucial.
Comparison of Different Gear Ratios
A typical manual transmission features a series of gears with varying ratios. Lower gears (like 1st and 2nd) have significantly lower ratios than higher gears (like 5th and 6th). This setup allows the vehicle to generate higher torque at lower speeds, facilitating acceleration and overcoming obstacles like hills or heavy loads. Higher gears, in contrast, yield higher speeds at a lower engine load and reduced fuel consumption.
Impact on Acceleration and Top Speed
Gear ratios directly affect acceleration and top speed. Lower gears, with their high torque output, are essential for rapid acceleration. As the vehicle gains speed, the driver shifts to higher gears, maintaining speed with less engine strain and increasing fuel efficiency. Top speed is ultimately limited by the highest gear ratio and the engine’s maximum rotational speed. The optimal gear selection at any given time depends on the vehicle’s speed, the road conditions, and the driver’s needs.
Impact on Fuel Efficiency
Gear ratios significantly impact fuel efficiency. Higher gears, with their lower engine speeds, are more fuel-efficient at highway speeds. Lower gears, however, are needed for quicker acceleration, but result in higher fuel consumption. The choice of gear in any given situation directly influences fuel economy, as optimal gear selection minimizes engine strain and enhances fuel utilization.
Gear Ratio Table
This table provides a comparative view of speed and torque output for each gear in a common manual transmission. Note that these values are approximate and can vary depending on the specific vehicle.
| Gear | Speed Output (approx.) | Torque Output (approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| 1st | Low | High |
| 2nd | Medium-low | Medium-high |
| 3rd | Medium | Medium |
| 4th | Medium-high | Medium-low |
| 5th | High | Low |
| 6th | Highest | Lowest |
Shifting Techniques and Gear Selection
Mastering manual transmission shifting is crucial for efficient driving and maximizing fuel economy. Proper gear selection directly impacts acceleration, fuel consumption, and overall driving experience. This section delves into techniques for smooth and efficient gear changes, emphasizing the importance of selecting the correct gear for various driving conditions.
Smooth Shifting Techniques
Effective shifting involves a combination of timing, force, and coordination. A smooth shift is characterized by minimal noise and a seamless transition between gears. The key is to avoid jerky movements and to maintain a consistent pressure on the clutch pedal.
- Controlled Clutch Engagement: Gradual release of the clutch pedal is paramount. Begin releasing the clutch pedal slowly as the engine speed increases. Match the engine speed to the gear’s requirements. This precise coordination prevents stalling or harsh shifts.
- Precise Timing: The ideal moment for shifting occurs when the engine’s speed aligns with the gear’s requirements. Practice recognizing the “sweet spot” by listening to the engine’s sound and feel of the vehicle’s acceleration.
- Controlled Throttle: Maintain a controlled throttle position throughout the shift process. Using the throttle appropriately helps the engine to seamlessly match the speed of the vehicle to the gear’s demands.
Importance of Gear Selection
Choosing the right gear is fundamental for optimizing performance and efficiency. Different driving scenarios necessitate specific gear selections.
- Acceleration: Lower gears provide more torque for rapid acceleration. The engine’s power is more readily transmitted to the wheels.
- Cruising: Higher gears allow the engine to operate at a lower RPM, improving fuel economy and reducing wear and tear.
- Uphill Driving: Lower gears provide the necessary torque to maintain speed and avoid stalling. Appropriate gear selection allows the vehicle to climb the incline without excessive strain.
Step-by-Step Shifting Guide, Understanding manual transmission gear ratios and their effects
This guide Artikels a systematic approach to shifting gears. Consistency and precision in these steps are essential.
- Assess the driving situation: Evaluate your speed, the road conditions, and the required acceleration or deceleration.
- Prepare for the shift: Reduce your speed to the appropriate range for the gear you intend to engage.
- Engage the clutch: Fully depress the clutch pedal to disengage the transmission.
- Select the gear: Shift the gear lever to the desired gear.
- Release the clutch gradually: Release the clutch pedal smoothly, ensuring that the engine speed matches the vehicle’s speed. Listen to the engine; it should smoothly accelerate.
- Adjust the throttle: Adjust the throttle position to maintain the desired speed.
Causes of Hard or Clunky Shifts
Hard or clunky shifts are often indicators of a problem that can be avoided.
- Incorrect clutch engagement: Failing to engage the clutch fully or releasing it too quickly can cause harsh shifts.
- Improper timing: Shifting too early or too late in relation to the engine’s speed results in a harsh transition.
- Lubrication issues: Insufficient lubrication can make shifting difficult.
- Mechanical problems: Gear synchronization issues or worn-out components can cause harsh shifts.
Optimal Gear Selection Table
The following table provides a general guideline for optimal gear selection based on driving conditions.
| Driving Condition | Optimal Gear |
|---|---|
| Accelerating | Lower gears (1st, 2nd, 3rd) |
| Cruising | Higher gears (4th, 5th) |
| Uphill | Lower gears (1st, 2nd, 3rd) |
| Downhill | Lower gears or use engine braking |
Effects of Gear Ratios on Performance
Gear ratios are fundamental to a manual transmission’s performance characteristics. They dictate how much engine power is translated into wheel speed at different speeds and loads. Understanding how these ratios influence acceleration, engine load, fuel economy, and handling is crucial for maximizing a vehicle’s capabilities and efficiency.
Acceleration and Gear Ratios
Gear ratios directly affect acceleration. Lower gear ratios provide higher torque multiplication, resulting in quicker acceleration from a standstill or during low-speed maneuvers. Conversely, higher gear ratios provide lower torque multiplication, resulting in slower acceleration but greater speed at higher RPMs. This relationship is evident in the need for lower gears when starting from a stop or climbing a steep hill.
Engine Load and RPM
Gear ratios influence the engine’s load and rotational speed (RPM). Lower gears impose higher engine load, meaning the engine works harder to propel the vehicle. Higher gears reduce engine load, allowing the engine to operate at lower RPMs for a given vehicle speed. This is why highway driving often utilizes higher gears to conserve fuel and engine life.
Fuel Consumption and Gear Ratios
Fuel consumption is significantly impacted by gear ratios. Higher gear ratios, enabling higher speeds with lower engine RPMs, typically lead to better fuel economy at constant speeds. Conversely, lower gears, which require higher engine RPMs for a given speed, result in higher fuel consumption. Optimal fuel efficiency is often achieved by selecting the appropriate gear for the current speed and driving conditions.
Gear Ratios and Terrain
Gear ratios play a crucial role in navigating diverse terrains. Steep hills demand lower gears to provide the necessary torque for climbing. Highways, conversely, benefit from higher gears to maintain a steady speed while minimizing engine load and maximizing fuel efficiency. Different gear ratios are tailored to specific terrains to optimize vehicle performance in various conditions.
Comparison of Vehicles with Different Gear Ratios
Vehicles with different gear ratios exhibit varying performance characteristics. Vehicles designed for off-road use often feature lower gear ratios for enhanced torque and traction. Conversely, vehicles designed for highway driving typically have higher gear ratios for optimal fuel economy at higher speeds. This difference in design reflects the diverse needs of different driving situations.
Impact of Gear Ratios on Acceleration Time
The relationship between gear ratios and acceleration time is complex and depends on various factors, including vehicle weight, engine power, and driver skill. The table below provides a general illustration of how gear ratios affect acceleration time at different speeds.
| Gear Ratio | Speed (mph) | Estimated Acceleration Time (seconds) |
|---|---|---|
| 1st | 0-20 | 5-8 |
| 2nd | 20-40 | 4-7 |
| 3rd | 40-60 | 3-6 |
| 4th | 60-80 | 2-5 |
| 5th | 80-100 | 1.5-4 |
Note: The acceleration time values are approximate and may vary significantly based on vehicle specifications and driving conditions. This table is intended as a general guideline and should not be used for precise calculations.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance: Understanding Manual Transmission Gear Ratios And Their Effects
Maintaining a manual transmission requires understanding its components and potential issues. Proper maintenance and diagnosis are crucial to prolonging the transmission’s lifespan and preventing costly repairs. Ignoring these aspects can lead to significant problems, affecting performance and potentially requiring costly replacements.
Common Manual Transmission Problems
Diagnosing issues with a manual transmission often involves a systematic approach. Symptoms can range from minor shifts to complete failure. Identifying the root cause requires attention to detail and a good understanding of how the transmission operates. Pinpointing the specific problem often necessitates a combination of observation, testing, and potentially professional assistance.
- Shifting Issues: Problems with shifting gears can manifest in various ways. A sticking or rough-shifting experience often indicates issues with the synchronizers, linkage, or the clutch itself. A grinding sound when shifting, for example, could point towards worn synchronizers, while a hard shift might suggest clutch problems.
- Clutch Problems: A slipping clutch, which manifests as a loss of power during acceleration, can be indicative of worn clutch friction material. A stiff or unresponsive clutch pedal might indicate problems with the clutch hydraulics or the pressure plate.
- Gear Ratio Issues: Sometimes, a gear ratio might feel excessively high or low in comparison to the expected performance. This could result from damaged gears, worn bearings, or misalignment within the transmission.
- Leaks and Fluid Problems: Fluid leaks can lead to reduced lubrication and damage to internal components. Low fluid levels or contaminated fluid can significantly impact performance and necessitate immediate attention.
- Noise and Vibration: Unusual noises or vibrations during operation, particularly when shifting gears, might indicate internal damage to gears, bearings, or shafts. These noises can range from a grinding sound to a whirring or knocking sound. The location and nature of the sound can be helpful in pinpointing the affected area.
Identifying Shifting Issues
Precisely diagnosing shifting problems requires careful observation and testing. Systematic checks can pinpoint the source of the issue. For example, a grinding noise during shifting usually indicates a problem with synchronizers, while a harsh shift often points towards clutch issues. It’s important to consider the specific symptoms, including the gear where the issue occurs and any associated sounds or vibrations.
Maintenance Procedures
Regular maintenance plays a vital role in the longevity of a manual transmission. Following a schedule for fluid changes, inspections, and component checks is essential. Proper lubrication ensures smooth gear operation, while regular inspections can prevent potential problems.
- Fluid Changes: Regular fluid changes, as recommended by the vehicle manufacturer, are critical for maintaining optimal transmission performance. Contaminated or degraded fluid can lead to premature wear and tear.
- Component Inspections: Regular inspections of components, such as the linkage, clutch, and synchronizers, are crucial for early detection of potential problems.
- Clutch Replacement: The clutch needs to be replaced when it shows signs of slipping or other issues. This typically happens after considerable wear and tear.
- Gear Ratio Adjustment: In some cases, adjustments to gear ratios might be necessary. This should be carried out by a qualified technician.
Impact of Improper Gear Selection
Choosing the wrong gear can lead to increased wear and tear on the transmission. For example, downshifting too late or too quickly during acceleration can cause the transmission to overheat and damage components. Driving at excessive speeds in a low gear can also cause undue strain.
Potential Issues with Specific Gear Ratios
Specific gear ratios can exhibit problems when mismatched with driving conditions. For instance, a high gear in a low-speed, steep-grade situation might result in a lack of power, while a low gear at high speed could cause excessive strain on the engine. Proper gear selection, in accordance with the driving situation, is paramount for avoiding these issues.
Troubleshooting Table
| Problem | Possible Solution |
|---|---|
| Grinding noise when shifting | Inspect and potentially replace synchronizers |
| Clutch slipping | Inspect clutch components and potentially replace friction material |
| Harsh shifting | Check the clutch linkage and adjust accordingly |
| Low fluid levels | Top up with the correct transmission fluid |
| Unusual noise or vibration | Inspect for damaged components; consult a mechanic |
Advanced Concepts and Considerations
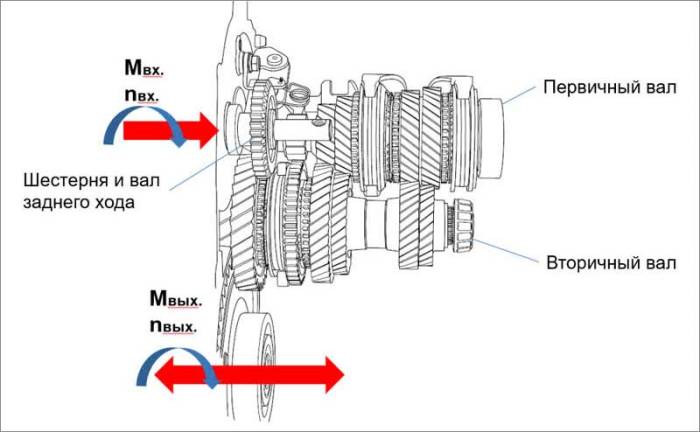
Source: drivertip.ru
Understanding manual transmission gear ratios goes beyond basic shifting techniques. Advanced concepts like overdrive gears, optimized ratio designs, and the impact on vehicle handling are crucial for a comprehensive understanding. This section delves into these complexities, highlighting the factors influencing gear ratio selection for various applications.Gear ratios are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Different vehicle types and driving conditions require tailored gear ratios to maximize performance and efficiency.
This section explores the nuances of this design process and the trade-offs involved.
Overdrive Gears and Fuel Efficiency
Overdrive gears are a crucial component in manual transmissions, offering enhanced fuel economy. These gears allow the engine to operate at a lower RPM for a given road speed, reducing fuel consumption. This is particularly beneficial for highway driving where maintaining a consistent speed at lower engine speeds is optimal. For example, a vehicle equipped with an overdrive gear can maintain a highway speed of 60 mph with the engine turning at a lower RPM than a vehicle without overdrive.
This directly translates to improved fuel efficiency.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Different Gear Ratio Designs
Various gear ratio designs cater to different vehicle applications. A high-ratio design, characterized by lower first gear ratios and higher top gear ratios, enhances acceleration but compromises top speed and fuel economy at higher speeds. Conversely, a low-ratio design, featuring higher first gear ratios and lower top gear ratios, excels in situations requiring significant torque output, such as off-roading, but may be less efficient on the highway.
Optimizing Gear Ratios for Specific Vehicle Applications
Gear ratios are meticulously optimized for specific vehicle applications. Race cars often feature gear ratios that prioritize acceleration, with lower top gear ratios and higher ratios in lower gears to maximize acceleration and maintain engine speed. Conversely, trucks may benefit from lower top gear ratios and higher first gear ratios to accommodate the greater load and torque demands of their operation.
Impact of Gear Ratios on Vehicle Handling Characteristics
Gear ratios directly influence vehicle handling characteristics. A higher gear ratio for a given speed results in a reduced engine speed. This often translates to reduced engine braking and increased ease of steering. Conversely, a lower gear ratio at a given speed results in a higher engine speed, which often translates to stronger engine braking and less responsive steering.
Factors Affecting Gear Ratio Design for Specific Applications
Several factors influence the design of gear ratios for specific applications. Consider racing vehicles, which require high-performance ratios that optimize acceleration, as opposed to off-road vehicles, which require low-ratio gears that prioritize traction and torque. Other factors include vehicle weight, engine power, and desired performance characteristics.
Comparison of Manual Transmission Designs and Their Gear Ratios
Different manual transmission designs can lead to varying gear ratio configurations. For example, a sequential transmission, often found in racing applications, allows for quicker and more precise gear changes, and the gear ratios are often optimized for acceleration. A traditional manual transmission, on the other hand, provides greater driver control, and the gear ratios are tailored to a broader range of driving conditions.
This comparison reveals the tailored approach to gear ratio design in each application.
| Transmission Type | Typical Gear Ratio Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Sequential | Optimized for quick shifts and acceleration | Racing, high-performance vehicles |
| Traditional Manual | Balanced for various driving conditions | General-purpose vehicles |

