Understanding Adverse Weather Conditions
Safe driving techniques for adverse weather conditions – Driving safely in adverse weather conditions requires a keen awareness of the specific challenges presented by various environmental factors. This understanding allows drivers to adapt their driving style and techniques to maintain control and prevent accidents. By recognizing the potential hazards and adopting appropriate precautions, drivers can significantly reduce the risk of incidents.
Rain
Rain significantly impacts road conditions, reducing visibility and increasing the risk of hydroplaning. Heavy rainfall can create standing water, which can obscure the road surface and make it difficult to judge the road’s contours. Drivers need to adjust their speed to maintain control.
Snow
Snowfall alters road surfaces, making them slippery and potentially dangerous. Accumulated snow and ice can create a very hazardous environment for drivers, as traction is drastically reduced. Reduced visibility due to falling snow also significantly compromises safe driving.
Ice
Ice is one of the most hazardous weather conditions for drivers. A thin layer of ice on a road surface can be almost invisible, but extremely dangerous. Ice reduces tire grip, making steering and braking significantly less effective. Sudden changes in road conditions can lead to loss of control.
Fog
Fog drastically reduces visibility, making it difficult to see other vehicles and road markings. Fog can cause drivers to lose situational awareness and can lead to a dangerous lack of reaction time. Fog often appears in clusters or pockets, making conditions even more unpredictable.
Strong Winds
Strong winds can impact vehicle handling, particularly for larger vehicles. Gusts of wind can push a vehicle off course, making it challenging to maintain a stable trajectory. Drivers need to be aware of wind conditions and adjust their driving accordingly.
Effects on Road Surfaces and Visibility
Adverse weather conditions significantly impact road surfaces, creating a variety of challenges for drivers. Rain can create a film of water, reducing friction between tires and the road, leading to hydroplaning. Snow and ice dramatically decrease traction, making braking and steering difficult. Fog drastically reduces visibility, hindering the driver’s ability to see other vehicles and road hazards.
Dangers Associated with Each Condition
Each adverse weather condition poses specific dangers to drivers. Rain can lead to hydroplaning, making it difficult to maintain control. Snow and ice greatly diminish traction, potentially causing loss of control and accidents. Fog severely restricts visibility, hindering reaction time and increasing the risk of collisions. Strong winds can impact vehicle stability, making it challenging to maintain a straight course.
Warning Signs and Indicators
Recognizing the warning signs of approaching adverse weather conditions is crucial for safe driving. Weather forecasts, changes in atmospheric pressure, and visual cues such as increased cloud cover or the appearance of falling rain or snow are all indicators of potential hazards.
Summary Table
| Weather Condition | Typical Effects on Driving | Recommended Precautions | Importance of Safety Measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rain | Reduced traction, hydroplaning risk, reduced visibility | Reduce speed, increase following distance, avoid sudden maneuvers | Essential for maintaining control and preventing accidents. |
| Snow | Reduced traction, slippery roads, reduced visibility | Slow down significantly, increase following distance, use caution when braking and turning | Crucial for preventing skidding and collisions. |
| Ice | Extreme reduction in traction, significant loss of control risk | Reduce speed dramatically, avoid braking and accelerating suddenly, increase following distance substantially | Critical for avoiding loss of control and accidents. |
| Fog | Extremely limited visibility, reduced reaction time | Turn on headlights, reduce speed significantly, use caution when approaching intersections and curves | Vital for maintaining safe distance from other vehicles and avoiding collisions. |
| Strong Winds | Increased vehicle instability, challenging to maintain course | Reduce speed, increase following distance, be aware of wind direction and intensity | Necessary for preventing loss of control and accidents, particularly for larger vehicles. |
Adjusting Driving Techniques for Different Conditions

Source: slideserve.com
Properly adjusting driving techniques is crucial for maintaining safety and control in adverse weather. Recognizing the specific challenges each condition presents and adapting your driving style accordingly can significantly reduce the risk of accidents. This section delves into the necessary modifications for various weather-related hazards.
Adjusting Driving Speed
Maintaining a safe speed is paramount in adverse weather. Lowering your speed allows for increased reaction time and greater control over your vehicle. Reduce speed progressively, anticipating potential hazards, rather than abruptly. For example, on icy roads, a speed reduction of 20-30 mph from typical driving speeds is often necessary. In heavy rain, reduce speed to maintain sufficient braking distance.
Adjusting Following Distance
Increased following distance is vital in adverse weather conditions. Reduced visibility and braking capabilities necessitate more space between vehicles. A good rule of thumb is to maintain a following distance of at least twice the normal distance. This extra space allows you to react to potential hazards or sudden stops.
Adjusting Braking Techniques
In adverse weather, typical braking techniques may not be effective. Avoid sudden braking maneuvers as they can lead to loss of control. Instead, use gentle, progressive braking to maintain vehicle stability. Employing anti-lock brakes (ABS) is essential, and the driver should be aware of the ABS system’s function. ABS will help prevent skidding.
If you feel the vehicle is skidding, ease off the brake pedal.
Adjusting Steering Inputs
Steering inputs should be smooth and gradual in slippery conditions. Avoid abrupt or excessive steering movements. In icy conditions, oversteering can lead to loss of control. Instead, make gradual, controlled turns, maintaining a steady course.
Maintaining Vehicle Control
Maintaining vehicle control is crucial in adverse weather. A key strategy is to anticipate potential hazards and adjust your driving accordingly. Keep a watchful eye on road conditions and other drivers, especially during periods of changing weather.
Strategies for Different Adverse Weather Conditions
| Weather Condition | Driving Speed | Following Distance | Braking and Steering Techniques |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ice | Significantly reduced, often 20-30 mph below normal | Double or triple the normal following distance | Gentle braking, avoid sudden maneuvers. Gentle steering inputs. |
| Heavy Rain | Reduced to allow for increased stopping distance | Increased following distance, consider twice the normal | Gentle braking, maintain control, anticipate hydroplaning. |
| Snow | Reduced speed based on snow accumulation and visibility | Increased following distance, maintain ample space | Gentle braking, avoid sudden movements. Maintain a smooth steering input. |
| Fog | Reduce speed to match visibility | Increase following distance, be mindful of reduced visibility | Be cautious with braking and steering. Maintain awareness of surroundings. |
Vehicle Preparation and Maintenance
Proper vehicle preparation is crucial for safe driving in adverse weather conditions. A well-maintained vehicle equipped for the conditions significantly reduces the risk of accidents and allows for a more controlled and predictable driving experience. This section details essential checks and maintenance procedures to ensure your vehicle is ready for various weather challenges.A pre-drive vehicle inspection, especially during inclement weather, is paramount.
This proactive approach can prevent potential hazards and keep you and others safe on the road. Checking tire pressure, tread depth, and lighting ensures proper vehicle handling and visibility. Maintaining wipers, defroster, and critical systems ensures a clear view and comfortable driving conditions.
Tire Pressure and Tread Depth
Adequate tire pressure and tread depth are critical for maintaining vehicle stability and traction in adverse weather. Low tire pressure reduces traction and increases the risk of skidding, especially on icy or snowy roads. Conversely, over-inflated tires can also negatively affect traction and handling. Regularly checking tire pressure and tread depth with a reliable gauge and visual inspection is essential.
Refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual for recommended tire pressure. Proper tire tread depth is crucial for optimal grip and should be checked against the legal minimums in your jurisdiction.
Lighting Systems
Proper lighting is vital for visibility in low-light or adverse weather conditions. Ensure all headlights, taillights, brake lights, and turn signals are functioning correctly. Check the bulbs for any damage or burnouts. If necessary, replace them with the correct type of bulb for optimal performance and visibility. Consider using supplemental lighting sources like driving lights in very low-visibility conditions, but remember to follow local regulations.
Wipers, Defroster, and Other Critical Systems
Effective wipers, a functioning defroster, and other essential systems are crucial for maintaining a clear view of the road. Ensure wipers are clean and in good working order, replacing them if necessary. Regularly check the defroster system to ensure it clears frost and ice effectively. Other systems like the heating and ventilation system should also be checked to ensure optimal comfort and visibility.
Inspect the fluid levels of the washer reservoir for sufficient windshield cleaning fluid.
Brake, Steering, and Other Critical Components
Maintaining proper functioning of brakes, steering, and other critical components is essential for safe driving. A thorough inspection of brake pads, rotors, and brake lines is crucial. The condition of the steering components should also be evaluated. Any unusual noises or vibrations during driving should be immediately investigated by a qualified mechanic. Regular maintenance, including oil changes and filter replacements, is vital to ensure optimal performance of critical systems.
Pre-Driving Checks for Adverse Weather
| Item to Inspect | Procedure to Follow | Potential Risks of Neglecting Checks | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tire Pressure | Use a gauge to check tire pressure against recommended values. | Reduced traction, increased risk of skidding, uneven tire wear. | Low tire pressure on icy roads can lead to loss of control. |
| Tire Tread Depth | Visually inspect tire tread depth using a penny test or other reliable methods. | Reduced traction, increased risk of hydroplaning, poor handling. | Low tread depth on wet roads can increase risk of hydroplaning. |
| Lighting System | Check all lights for functionality and damage. | Reduced visibility, increased risk of accidents for other drivers. | Faulty headlights can severely impact night driving safety. |
| Wipers and Defroster | Ensure wipers are clean and defroster functions correctly. | Impaired visibility, reduced control over the vehicle. | Inadequate windshield clearing can lead to reduced visibility and poor reaction times. |
Emergency Preparedness and Response
Source: windows.net
Adverse weather conditions can lead to unexpected and potentially dangerous situations on the road. Understanding how to respond appropriately in emergencies is crucial for ensuring your safety and the safety of others. This section Artikels essential emergency preparedness and response strategies for various challenging driving scenarios.
Potential Emergency Situations
Adverse weather conditions can create a range of hazardous situations, impacting driving safety significantly. These situations include, but are not limited to, hydroplaning, skidding, reduced visibility, and encountering other vehicles involved in accidents. Proper preparation and response are critical to mitigate risks and maintain control in these circumstances.
Hydroplaning Response
Hydroplaning occurs when a vehicle’s tires lose contact with the road surface due to a layer of water. Maintaining a steady speed and avoiding sudden maneuvers are key. Gradually easing off the accelerator and steering gently in the direction you want to go are essential actions. Do not apply the brakes. If the vehicle begins to fishtail, gradually apply the brakes while steering in the direction of the skid.
Skidding Response, Safe driving techniques for adverse weather conditions
Skidding, particularly on icy or snow-covered roads, is another critical concern. Recognizing the type of skid (front-end or rear-end) and reacting appropriately is vital. Release the accelerator and steer in the direction the vehicle is skidding. Avoid braking and accelerating. In a rear-end skid, easing off the gas and steering in the direction of the skid will help regain control.
Maintaining a Safe Following Distance
Maintaining a safe following distance is crucial in all driving conditions, especially during adverse weather. A greater following distance allows more time to react to unexpected situations. In adverse weather, doubling or tripling the normal following distance is often recommended. This is critical for stopping distance, as braking distances in inclement weather conditions can be significantly longer than in dry conditions.
Poor Visibility Response
Reduced visibility due to fog, heavy rain, or snow significantly impairs driver awareness. Adjusting driving speed to maintain control and visibility is paramount. Turn on your headlights, even during the daytime, and use your windshield wipers effectively. Be cautious of pedestrians or other road users, as their visibility may be equally reduced.
Emergency Procedures
Emergency procedures are vital for responding to unexpected incidents on the road. Safety is paramount when pulling over. Find a safe location, away from traffic and obstacles, to pull over. Activate your hazard lights and place reflective triangles. Utilize any emergency equipment (first-aid kit, jumper cables, etc.) as needed.
Contact emergency services immediately if necessary. The emergency services can be contacted via emergency telephone numbers or mobile phone applications.
Emergency Situation Response Guide
| Emergency Situation | Appropriate Response | Safety Precautions | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydroplaning | Ease off the accelerator, steer gently in the direction you want to go, avoid braking. | Maintain a safe following distance, avoid sudden maneuvers. | Gradually regain control, assess the situation. |
| Skidding | Release the accelerator, steer in the direction the vehicle is skidding, avoid braking. | Adjust speed according to conditions, maintain a safe following distance. | Stay calm and focus on regaining control. |
| Poor Visibility | Reduce speed, turn on headlights, use windshield wipers effectively. | Increase following distance, be cautious of pedestrians. | Monitor road conditions and adjust driving accordingly. |
| Vehicle Breakdown | Pull over to a safe location, activate hazard lights, use reflective triangles. | Stay with your vehicle, contact emergency services. | Assess your situation, gather essential items. |
Safe Driving Practices in Specific Conditions

Source: co.uk
Driving safely in adverse weather conditions requires a proactive and adaptable approach. Recognizing the specific challenges presented by heavy rain, snow, ice, fog, and strong winds is crucial for maintaining control and minimizing risks. This section Artikels strategies for safe driving in various challenging situations.
Driving in Heavy Rain
Maintaining visibility and tire grip are paramount during heavy rain. Reduced visibility necessitates adjusting speed and increasing following distance. Drivers should avoid sudden braking or acceleration, which can lead to loss of control. Driving too fast for the conditions is a frequent cause of accidents in heavy rain. Excessive speed reduces the time available to react to hazards and increases the risk of hydroplaning.
- Reduce Speed: Slow down significantly to accommodate the reduced visibility and potential for hydroplaning. Adjust your speed based on the intensity of the rain.
- Increase Following Distance: Maintain a much greater distance than usual between your vehicle and the one in front. This allows more time to react to sudden braking or changes in the road conditions.
- Avoid Sudden Braking or Acceleration: These actions can lead to loss of control, particularly on wet roads. Brake smoothly and gradually accelerate.
- Use Low Beams: Use low beams to maximize visibility. High beams are less effective in heavy rain.
Driving in Snow or Ice
Driving on snow or ice requires a completely different approach compared to dry roads. Maintaining traction and avoiding sudden movements are crucial. Adjusting your speed and driving style for these conditions is essential for safety. Anticipating potential hazards and adapting your driving habits can significantly minimize risks.
- Reduce Speed Significantly: Lower your speed considerably to allow more time to react to unexpected situations.
- Increase Following Distance: Maintain a substantially larger following distance to react to sudden braking or loss of traction.
- Avoid Sudden Braking or Acceleration: Avoid abrupt maneuvers, as these are likely to lead to loss of control on slippery surfaces.
- Use Winter Tires (if available): Winter tires offer superior traction in snow and ice conditions. Their use is strongly recommended in these circumstances.
Driving in Fog
Fog significantly reduces visibility, making driving hazardous. Adjusting speed and maintaining a safe following distance are crucial to prevent collisions. Using low beams or fog lights is essential for visibility. Driving slowly and cautiously is paramount in foggy conditions.
- Reduce Speed: Driving slower than usual will allow for more time to react to potential hazards and obstacles.
- Increase Following Distance: A larger following distance provides more time to react to sudden braking or changes in the road conditions.
- Use Low Beams or Fog Lights: Utilize low beams or fog lights to improve visibility. High beams are less effective in fog.
- Be Aware of Visibility Limitations: Recognize that your visibility is significantly reduced and adjust your driving accordingly.
Driving in Strong Winds
Strong winds can affect vehicles, especially those with less stable aerodynamic profiles. Maintain a safe following distance and be cautious of wind gusts. Adjust your speed to accommodate wind conditions. High-profile vehicles are more susceptible to being affected by strong winds.
- Reduce Speed: Adjust speed based on the intensity of the wind.
- Increase Following Distance: Maintain a larger following distance to accommodate sudden changes in wind gusts.
- Avoid Overtaking: Do not attempt to overtake another vehicle, especially in strong winds, as this can be dangerous.
- Watch for Vulnerable Vehicles: Be aware of vehicles that are more susceptible to wind gusts, like motorcycles and high-profile cars.
Safe Driving Practices Table
| Adverse Weather Condition | Appropriate Driving Behavior | Potential Risks | Preventive Measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy Rain | Reduce speed, increase following distance, avoid sudden maneuvers | Hydroplaning, reduced visibility, loss of control | Use low beams, maintain a safe distance, adjust speed for intensity of rain |
| Snow/Ice | Reduce speed drastically, increase following distance, use winter tires (if available) | Loss of traction, skidding, reduced visibility | Avoid sudden movements, drive slowly, maintain a significant following distance |
| Fog | Reduce speed, increase following distance, use low beams or fog lights | Reduced visibility, collisions | Be cautious, maintain focus, avoid unnecessary lane changes |
| Strong Winds | Reduce speed, increase following distance, avoid overtaking | Vehicle instability, loss of control, increased risk of collisions | Be aware of wind gusts, maintain control of the steering wheel, maintain vigilance |
Visual Aids and Information Presentation: Safe Driving Techniques For Adverse Weather Conditions
Visual aids are crucial for effectively communicating safe driving techniques in adverse weather conditions. Clear and concise visuals can significantly enhance understanding and retention of critical information, promoting safer driving habits. This section details the design of several visual aids to illustrate key aspects of safe driving during various weather situations.
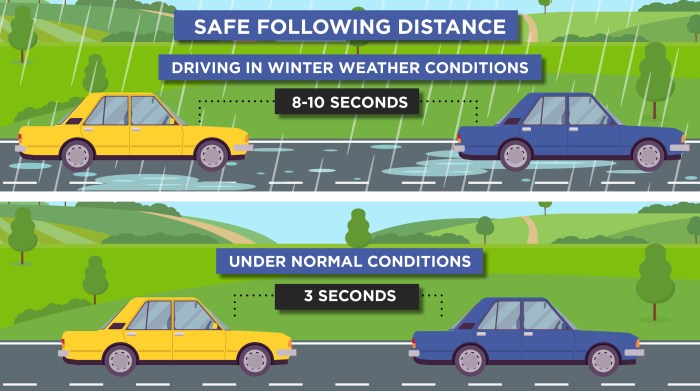
Safe Following Distance in Different Weather Conditions
Visual representation of safe following distances is essential to illustrate the impact of weather on reaction time and braking distances. A graphic could depict a series of cars on a road, with each car progressively further back from the preceding vehicle. Different weather conditions (e.g., light rain, heavy rain, snow, fog) would be represented by varying degrees of fading or blurring behind the car in front.
The distance between each car would be clearly marked, highlighting the need for increased following distance in adverse conditions. This visual would demonstrate the necessity of a longer reaction time and braking distance required in various weather conditions.
Proper Braking Techniques on Slippery Surfaces
A visual aid depicting proper braking techniques on slippery surfaces would show a car approaching a curve or a hazard. The graphic would illustrate the controlled braking technique, where the driver gradually applies the brakes while steering in a straight line. The visual would demonstrate the avoidance of harsh braking, which could lead to loss of control. The image should clearly contrast the controlled braking method with a scenario illustrating uncontrolled braking on a slippery surface, resulting in skidding or loss of vehicle control.
Safe Handling of a Skidding Vehicle
A graphic illustrating how to safely handle a skidding vehicle would show a car starting to skid. The visual would guide the driver to gently counter-steer in the direction of the skid. This should be depicted with arrows or other visual cues showing the correct steering input needed to regain control. A comparison could be made between the correct action of counter-steering and the incorrect reaction of over-steering, which would further exacerbate the skid.
The visual aid should also display the importance of releasing the accelerator and applying the brakes, if necessary, to regain control.
Proper Tire Tread Depth for Safe Driving
A visual aid showcasing proper tire tread depth would be a graphic of a tire, highlighting the minimum tread depth recommended by the government or regulatory agencies. The graphic would show a section of the tire’s tread pattern with various tread depths, including a correctly sized tire and tires with insufficient tread depth. Different levels of tread depth (e.g., worn, acceptable, and excellent) could be displayed with varying shades of gray or different colors, with clear labels indicating the minimum acceptable tread depth.
This visual aid will emphasize the crucial role of sufficient tire tread in maintaining vehicle traction and stability, especially during adverse weather conditions.

