Introduction to Hill Starts

Source: goodcar.com
Learning manual driving techniques for hill starts – Hill starts present a unique challenge in manual driving, requiring careful consideration of vehicle dynamics and control. The steep incline of a hill can cause the vehicle to roll backward if not handled correctly. This necessitates a precise sequence of actions to maintain control and prevent unwanted movement.Mastering hill start techniques is crucial for safe and efficient driving, particularly in challenging conditions like steep inclines or slippery surfaces.
It ensures smooth departures, preventing accidents and potential damage to the vehicle. A strong understanding of the process, including the specific methods employed, is paramount for both novice and experienced drivers.
Hill Start Methods Overview
Different methods exist for executing hill starts in manual vehicles, each with its own set of steps. These methods often involve manipulating the clutch, gear selection, and brake application to maintain control during the initial stages of motion. A common strategy is to maintain pressure on the brakes while engaging the clutch, and then smoothly releasing the brakes and simultaneously disengaging the clutch.
Key Components of a Hill Start, Learning manual driving techniques for hill starts
Understanding the precise sequence of actions is essential for a smooth and controlled hill start. This involves a coordinated effort involving various components of the vehicle and driver’s actions.
| Component | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Foot position | Maintaining consistent pressure on the brake pedal is critical during the initial stages. The driver should also have their right foot prepared to depress the accelerator if necessary. | Firm pressure on the brake, ready to release. |
| Clutch engagement | Gradual engagement of the clutch is essential. This allows the engine to build torque without the wheels spinning. | Slowly release the clutch pedal, maintaining a controlled acceleration. |
| Gear selection | Selecting the correct gear is paramount. The proper gear should provide sufficient engine torque for the incline without excessive wheel spin. | Usually first gear is used for a hill start. |
| Steering control | Steering should be maintained in a controlled manner, with minimal movement. Focus should be on maintaining a straight path. | Maintain the desired path without unnecessary steering input. |
Basic Techniques for Hill Starts
Mastering hill starts is crucial for safe and confident driving, especially on inclines. Proper technique ensures smooth transitions and prevents rolling backward, a common issue for novice drivers. Understanding the interplay between clutch, gear, and handbrake is key to achieving controlled acceleration uphill.
Fundamental Steps for a Smooth Hill Start
A controlled hill start involves a series of coordinated actions. Gradual application of the clutch and consistent engagement of the handbrake are essential. The sequence of actions must be precise to maintain stability and prevent the vehicle from rolling backward.
- Assess the Slope: Before starting, evaluate the incline. A steeper slope necessitates more caution and a firmer handbrake application.
- Engage the Handbrake: Firmly apply the handbrake to prevent the vehicle from rolling backward. A consistent and sufficient handbrake application is crucial. This is often overlooked and can lead to incidents.
- Select First Gear: Place the vehicle in first gear. Ensuring the gear is correctly selected is a critical step.
- Release the Handbrake Slightly: Gradually release the handbrake, maintaining some tension to prevent sudden movement. The amount of handbrake release needs to be controlled.
- Engage the Clutch: Depress the clutch pedal slowly, allowing the engine to start smoothly. The clutch must be engaged progressively to avoid a jerky start.
- Release the Clutch Gradually: Slowly release the clutch while gently pressing the accelerator. This process allows the engine to supply enough power for the hill ascent without jerking.
- Maintain Control: Keep your foot on the accelerator to maintain the vehicle’s position on the incline. Continue monitoring the vehicle’s movement.
- Release the Handbrake Completely: Once the vehicle is moving steadily uphill, completely release the handbrake.
The Role of the Clutch in Hill Starts
The clutch is instrumental in controlling the vehicle’s movement during a hill start. It acts as a connection between the engine and transmission, allowing controlled acceleration. Proper clutch control is crucial for avoiding jerky movements or stalling.
- Smooth Clutch Engagement: Gradual clutch engagement prevents the vehicle from rolling backward as the engine’s power engages the drive wheels.
- Controlled Release: A slow and gradual release of the clutch ensures a smooth acceleration, preventing the vehicle from lurching. A jerky release of the clutch can lead to loss of control.
- Clutch Pedal Pressure: Maintaining consistent clutch pedal pressure throughout the process is critical for a smooth transition. This consistent pressure aids in controlled acceleration.
Importance of Handbrake Engagement Technique
Proper handbrake engagement is crucial for safety during hill starts. It prevents the vehicle from rolling backward while the driver prepares the vehicle for acceleration.
- Firm Engagement: The handbrake must be firmly engaged to maintain the vehicle’s stationary position on the incline.
- Consistent Tension: Maintaining consistent tension on the handbrake during the process ensures the vehicle doesn’t move backward. Consistent tension is key.
- Gradual Release: Gradually releasing the handbrake, in conjunction with clutch and accelerator, is important to ensure smooth acceleration. Release should be gradual to prevent sudden movement.
Step-by-Step Hill Start Procedure
This procedure Artikels the steps for a basic hill start. Following these steps precisely helps in achieving a smooth and controlled start.
- Position the Vehicle: Park the vehicle on the incline, ensuring the handbrake is fully engaged. Position yourself correctly.
- Gear Selection: Select first gear. Confirm the gear selection.
- Handbrake Engagement: Apply the handbrake firmly to secure the vehicle. Confirm the handbrake is fully engaged.
- Clutch Engagement: Depress the clutch pedal, then gradually release the handbrake while maintaining tension.
- Accelerator Engagement: Gradually release the clutch while gently pressing the accelerator. Start with light pressure and adjust as needed.
- Maintaining Control: Maintain steady acceleration and control the vehicle on the incline. Monitor the vehicle’s progress.
- Handbrake Release: Release the handbrake completely once the vehicle is moving steadily uphill.
Comparison of Hill Start Methods
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Hill Start | Simple to learn, widely applicable. | Requires consistent practice for smooth transitions. |
| Techniques for Steep Inclines | Effective on very steep hills. | May be more complex to master for beginners. |
Advanced Hill Start Techniques

Source: evanshalshaw.com
Mastering hill starts goes beyond the basics. Advanced techniques optimize control and safety, particularly on challenging inclines and surfaces. Understanding these methods empowers drivers to handle a wider range of driving situations with greater confidence.Advanced techniques refine the basic principles, allowing for more controlled and predictable hill starts in diverse conditions. They build upon the fundamental understanding of clutch control, gear selection, and braking, allowing for smoother transitions and increased safety.
Utilizing Higher Gears
Selecting a higher gear for a hill start can be advantageous in certain situations. A higher gear reduces the engine’s workload, potentially making the initial push easier. This is especially helpful on gentle inclines, where the engine can more readily maintain traction. However, the choice of a higher gear needs to be carefully balanced against the slope of the hill and the vehicle’s capabilities.
Adjusting for Hill Slope
The steepness of the hill significantly impacts the hill start technique. Steeper hills require a more aggressive approach, including firmer clutch control and possibly using a lower gear to maintain adequate engine braking. Conversely, on gentler slopes, a higher gear might be sufficient. Drivers should adapt their technique to match the specific incline.
Handling Different Surfaces
Surface conditions play a crucial role in hill starts. Gravel surfaces, for instance, offer less traction than paved roads. Drivers need to be extra cautious and use less aggressive clutch engagement to prevent wheel slippage. On icy surfaces, maintaining controlled movement and avoiding sudden maneuvers is paramount. Applying light braking and a smooth clutch engagement are vital in such situations.
Adjustments for Varying Vehicle Characteristics
Vehicle weight and power output influence the ideal hill start approach. Heavier vehicles require more assertive control over the clutch and brakes to maintain traction. Vehicles with lower power outputs might need to use a lower gear to compensate for the reduced engine torque. Understanding these factors ensures the most effective technique for each vehicle.
Tackling Steep Hills
Steep hills present a greater challenge. Drivers must utilize a combination of precise clutch control, gradual release of the brake, and a lower gear. Engine braking is a key factor in managing the vehicle’s momentum. A slight delay in releasing the brake, to allow the engine to engage, can help prevent the vehicle from rolling backward. Using a lower gear helps in maintaining control, especially when the slope is very steep.
Comparison of Advanced Hill Start Methods
| Method | Gear Selection | Clutch Control | Braking | Surface Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Higher Gear (Gentle Slope) | Higher gear (3rd or 4th) | Gentle engagement | Release gradually | Paved, gentle inclines |
| Lower Gear (Steep Slope) | Lower gear (1st or 2nd) | Firm engagement | Release gradually, but with more caution | Steep inclines, uneven surfaces |
| Gravel/Icy Surfaces | Appropriate gear (consider reduced traction) | Very gentle engagement | Very light braking | Gravel, ice, or other surfaces with reduced traction |
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them: Learning Manual Driving Techniques For Hill Starts
Learning hill starts effectively requires mastering proper technique, and unfortunately, many drivers encounter common errors. Understanding these pitfalls and their remedies will significantly enhance your skill and confidence behind the wheel. Recognizing these mistakes and the reasons behind them is crucial for improvement.
Common Errors in Hill Starts
A meticulous understanding of common mistakes is vital for safe and proficient hill starts. These errors often stem from a lack of focus, insufficient practice, or misinterpreting the nuances of the technique. Knowing what to look out for allows you to refine your approach and eliminate these pitfalls.
- Mistake 1: Releasing the clutch too early. This common error frequently arises from impatience. Drivers might feel a slight hesitation and prematurely release the clutch, leading to the vehicle rolling backward. The vehicle’s momentum can overwhelm the brakes, leading to a loss of control and a potential accident.
- Mistake 2: Insufficient braking. Insufficient braking pressure on a steep incline can result in the vehicle rolling backward. This is often due to underestimating the incline’s steepness or the vehicle’s weight, leading to a failure to maintain control.
- Mistake 3: Incorrect gear selection. Choosing the wrong gear can affect the vehicle’s ability to maintain stability during the hill start. Selecting a gear that is too high or too low can create a balance issue, making the vehicle more prone to rolling backward or stalling.
- Mistake 4: Ignoring the handbrake. The handbrake is an essential tool in controlling the vehicle’s movement during a hill start, particularly on steep inclines. Drivers often overlook its crucial role, and forgetting to apply or maintain the handbrake during the start can cause the vehicle to roll backward.
- Mistake 5: Incorrect foot placement. Incorrect foot positioning on the pedals can lead to an unstable and uneven control of the vehicle during the hill start. This mistake is often associated with a lack of coordination between the clutch, brake, and accelerator.
Solutions to Avoid Common Errors
Addressing these common errors requires a proactive approach. By understanding the reasons behind these mistakes, drivers can take steps to avoid them in the future. Consistent practice and a clear understanding of the process are essential.
- Addressing Clutch Release: Gradual clutch release is key. Practice a smooth, controlled release to prevent the vehicle from rolling backward. Use a controlled release technique to avoid this.
- Optimizing Braking: Apply firm, consistent braking pressure, considering the incline’s steepness and the vehicle’s weight. Ensure the vehicle is adequately slowed before releasing the clutch to minimize rolling back.
- Proper Gear Selection: Choose the correct gear for the hill’s incline. Selecting the appropriate gear provides the ideal balance between traction and control during the hill start. This involves considering the steepness of the hill and the vehicle’s weight.
- Utilizing the Handbrake: Maintain consistent handbrake pressure during the initial moments of the hill start. This provides a crucial safety net against backward movement, especially on steep hills.
- Perfecting Foot Placement: Maintain a firm but relaxed grip on the pedals to ensure balanced control. Position your feet strategically on the clutch, brake, and accelerator pedals for optimal coordination.
Practice and Refinement
Mastering hill starts requires consistent practice and a structured approach. This section details effective practice scenarios, safe environments, and the importance of adjusting practice based on individual skill levels. Understanding how to adapt your practice is key to achieving proficiency and building confidence.Effective practice is not just about repetition; it’s about understanding the nuances of the process and refining your technique.
A well-designed practice plan can accelerate your learning and help you identify and address any weaknesses in your skills.
Practice Scenarios for Improving Hill Start Skills
Consistent practice in various scenarios is crucial for developing strong hill start skills. Practice on different inclines, from gentle slopes to steeper hills, allows you to adapt your technique to varying conditions. Practice on different types of surfaces, like smooth asphalt and slightly uneven surfaces, will enhance your adaptability and responsiveness. Varying road conditions, including wet or icy surfaces (where appropriate and safe), can help you understand how to adjust your techniques.
Consider practicing with different vehicles (if possible), as the weight and responsiveness can impact your technique.
Tips for Practicing Hill Starts in a Safe Environment
Safety is paramount when practicing hill starts. Select a location with minimal traffic and pedestrians. Ensure adequate space for maneuvering and performing the hill start procedure without risk of collision. Employ parking brakes or hand brakes effectively. Be mindful of other vehicles and pedestrians in the area.
Choose a suitable time of day, avoiding rush hours, and ensuring visibility. Always prioritize safety, and if conditions feel unsafe, postpone the practice session.
Importance of Consistent Practice to Build Confidence and Proficiency
Consistent practice, even in short intervals, is essential for developing and refining your hill-starting skills. Regular practice sessions will reinforce the correct techniques, leading to increased confidence and proficiency. This regular practice allows for adjustments and refinements based on observed mistakes and successes. By maintaining consistency, you can progressively improve your skills and build the confidence to handle varied hill start situations.
Adjusting Practice Based on Individual Skill Levels
Tailoring practice to individual skill levels is crucial for effective learning. Beginners should focus on mastering the fundamental techniques, practicing on gentle inclines, and gradually increasing the slope. Intermediate drivers can incorporate more complex scenarios, such as practicing on steeper inclines and handling varying road conditions. Advanced drivers can concentrate on fine-tuning their technique, practicing in challenging environments and adapting to unexpected situations.
A personalized approach ensures consistent progress.
Structured Practice Plan
| Day | Exercise | Difficulty | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Basic Hill Start on a gentle incline | Beginner | 15 minutes |
| 2 | Hill start with clutch control practice | Beginner | 20 minutes |
| 3 | Hill start on a moderate incline, varying speeds | Intermediate | 25 minutes |
| 4 | Hill start with braking and acceleration | Intermediate | 20 minutes |
| 5 | Hill start on a steep incline, with multiple attempts | Advanced | 30 minutes |
| 6 | Hill start on different surfaces (e.g., wet, icy) | Advanced | 25 minutes |
| 7 | Review and evaluation | All Levels | 15 minutes |
Vehicle-Specific Considerations
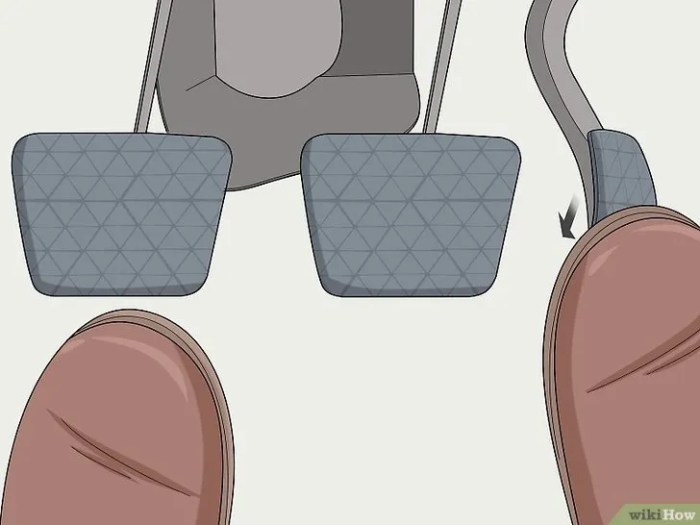
Source: wikihow.com
Mastering the hill start involves understanding how different vehicle types and their features impact the technique. This section delves into vehicle-specific nuances, exploring how various designs and electronic aids influence the hill start procedure.Different vehicles respond to the same technique in subtly different ways, due to variations in engine characteristics, transmission designs, and weight distribution. Understanding these differences allows for a more precise and efficient hill start in any given vehicle.
Varying Techniques Based on Vehicle Type
Various vehicle types exhibit different responses to the hill start technique. Factors like engine power, transmission type (automatic, manual), and vehicle weight affect the difficulty and required adjustments.
Specific Features Affecting Hill Start Procedures
Certain vehicle features significantly impact hill start procedures. For example, vehicles with a high center of gravity may require more careful control during the initial phase of the hill start.
- Engine Characteristics: Vehicles with powerful engines may require less time or effort to maintain traction, while those with less powerful engines may necessitate a more controlled approach. The engine’s torque output is a key consideration. Higher torque allows for a quicker and more controlled release of the clutch, reducing the risk of rolling back.
- Transmission Design: Automatic transmissions, with their inherent gear shifting mechanisms, might offer a slightly different experience compared to manual transmissions. The automatic transmission’s ability to maintain a consistent power output can influence the stability during the hill start. Manual transmissions require precise clutch control to prevent the vehicle from rolling backward.
- Weight Distribution: Vehicles with a heavier weight distribution may need more time to maintain traction. The weight distribution directly affects the stability of the vehicle, and the center of gravity is critical. Vehicles with a higher center of gravity require more controlled and precise clutch engagement and braking to prevent rolling backward.
Role of Electronic Aids in Hill Starts
Electronic aids like hill-hold assist (HLA) significantly simplify the hill start procedure in modern vehicles. HLA systems provide a temporary braking function, preventing the vehicle from rolling backward, and making the start smoother and more reliable.
- Hill-Hold Assist (HLA): HLA automatically applies a short braking force to maintain the vehicle’s position on an incline while the driver’s foot is on the brake pedal, freeing the driver to shift into drive and release the brake. This reduces the risk of rolling back, making hill starts safer and easier, especially for less experienced drivers. HLA is crucial in vehicles with features like a high center of gravity.
Examples of Varying Vehicle Designs
Different vehicle designs influence hill start techniques. Consider a compact car versus an SUV. A compact car, due to its lower weight and center of gravity, may require less braking effort and a quicker release of the clutch. An SUV, with its higher weight and center of gravity, necessitates a more cautious approach, potentially requiring a longer period of brake application before releasing the clutch.
| Vehicle Type | Engine Characteristics | Transmission | Weight Distribution | Hill Start Technique |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compact Car | Lower power | Manual or Automatic | Lower center of gravity | Quicker clutch release, shorter braking period |
| SUV | Higher power | Manual or Automatic | Higher center of gravity | More cautious clutch release, longer braking period |
| Heavy-Duty Truck | High Torque | Manual | High weight, high center of gravity | Extended braking period, precise clutch control, potentially using a handbrake to hold |

